Change Permissions Linux Folder to Upload Files
Learning how to alter files permissions on Linux should exist nowadays on your Linux topic list because you tin prevent security issues that could compromise your system.
Change files permissions on Linux.
Thechmodcontrol permits users to change file permissions on Linux, like reading and write in Unix systems. In this postal service, we will explain to you how to modify file and folder permissions withchmod.
In addition, the chmod command is the most applied and most effortless way to change these file permissions.
Permission on Linux – How it works
Earlier going deep on the command line to change file permissions on Linux, briefly innovate how it works the permissions on Linux.
When we talk nigh a Linux system, every file and binder has divers the admission rights for the file owner, the members of a group of similar users, and everybody else. You lot can specify reading, writing, or executing a file (for case, executing a shell script file).
To view the permission assigned for a specific file, nosotros can utilize thelscontrol. For example, we will examine the bash program placed in the /usr/bin folder.
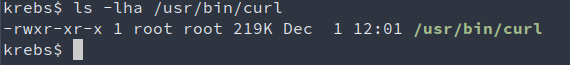
Here we tin can run into:
- The file "/usr/bin/curl" owner is the user "root."
- The superuser (root) has admission to write, read and execute.
- The root is the group owner of this file.
- Users that belong to the group "root" also can execute and read and this file.
- Anyone can read and execute this file.
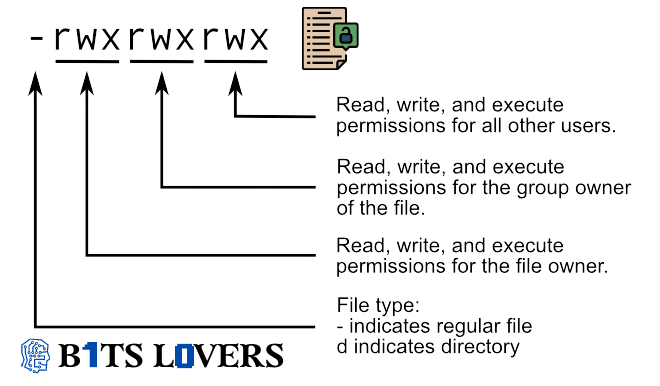
In the chart below, we meet how the first part of the listing is described. It consists of a letter of the alphabet showing the file type, attended by three collections of three characters representing READ, WRITE, and EXECUTION permission for the Owner, Grouping, and everybody else.
How to use the Chmod command to Change files permissions on Linux.
First, let'south talk about the octal annotation and symbols .
The chmod command is applied to change files permissions on Linux and also for folders. We specify the permission settings and the file or folder to change it. There are two methods to decide the permissions.
rwx — — = 111 000 000
rw- rw- rw- = 110 110 110
rwx rwx rwx = 111 111 111
r– = 100 in binary = 4
r-x = 101 in binary = 5
rw- = 110 in binary = vi
rwx = 111 in binary = vii
Finally, allow's see how to use the chmod.
The basic syntax is:
chmod <permission> <file_name>
How to define and change files permissions on Linux using Symbolic Mode
To define permission using alphanumerical characters, you'll necessitate limiting accessibility for the user/possessor(u), Grouping(one thousand), and others (o).
Specify the initial letter for every form, followed past the equal symbol(=) and the initial letter of theRead,Write, and/or execute(x) rights. Also, we have(a),which meansALL, identical tougo.
To configure a file so if anyone can read, write, and execute, the command is:
chmod u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx <file-proper noun>
Use the post-obit command:
chmod u=rw,thou=r,o=r test.txt
More Options:
chmod [OPTIONS] [ugoa…][-+=]grants…[…] <file-proper noun>.
The following ready of flags ([-+=]), the operation flags, sets whether the permissions are to be removed, added, or placed:
– Eliminates the specified permissions.
+ Attaches specified permissions.
= Modifies the current permissions to the divers permissions. If no permissions are defined following the = symbol, whatever permissions from the chosen user class are excluded.
The grants (grants…) can exist explicitly set utilizing either zero or more of the subsequent letters: r, due west, ten, X, due south, and t. Use a single letter of the alphabet from the fix u, yard, and o when copying grants from ane to a different user's class.
When placing permissions for more than 1 user class ([…]), use commas (without spaces) to leave the symbolic modes.
Hither are fantabulous samples of how to practice the chmod command in symbolic mode:
Give the pausers of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it:
Remove the execute permission for all users:
Encounter more examples:
Repulsively eliminate the write permission for boosted users:
chmod -R o-w <folder-name>
Making a file executable in linux
Let's see how we can configure a file to let the states to execute that file. So, the following examples alter the file permissions so that whatever user can perform the file "run-fill-in.sh":
Directory permission in linux
The approach to change files permissions on Linux also works for directories with thechmodcontrol. Also, nosotros can apply the octal note to set permissions. However, the purpose of the r, w, and 10 properties is some other:
- r – Enables the contents of the directory to be listed if the ten property is besides set.
- w – Enables files inside the directory to be created, deleted, or renamed if the x property is besides ready.
- ten – Enables a directory to be opened (i.e., cd folder-name).
Instance of some applicable settings for directories:
700 (rwx——) -> The directory owner has complete admission. Nobody else has any rights. This setting is helpful for folders that but the Owner may handle and must be held hole-and-corner from others.
755 (rwxr-xr-x) -> The directory possessor has complete admission. All others may list the directory but cannot generate files nor remove them. This setting is typical for directories that you want to share with actress users.
777 (rwxrwxrwx) -> No limitations on permissions. Everyone may list files, create new files in the folder and remove files in the directory. Oft not a skilful approach.
Octal permission
Any File and Binder contain 8-bit data that manages the permissions. For example, in its principal binary form, 000 indicates that no rights.
When you lot place a "Read" permission, it attaches 4-bit to the data, giving information technology "100" (in binary format) or a "4" in the standard decimal format. Assigning a "Write" permission will suspend 2-bit to the data, giving it "010" and "2" in decimal mode. Finally, setting an "Execute" rights appends 1-chip to the information, which will result in "001" or "ane" in a decimal format. In brief:
- Read is like to "iv."
- Write is similar to "2."
- Execute is similar to "1."
In a nutshell, setting permissions is basic math. For instance, to select "Read and Write" grants, we alloy 4 and 2 to get 6. Then, of class, there are other alterations:
- 0: No permission
- ane: Execute
- 2: Write
- iii: Write and Execute
- 4: Read
- 5: Read and Execute
- 6: Read and Write
- vii: Read, Write, and Execute
The outset number represents the Owner, the second number to the Group, and the third to Others. Here are some of the regularly used for permissions:
- 755. This set of grants is generally used by web servers. The Owner has full the permissions to read, write and execute. Anybody else can read and run but cannot make modifications to the file.
- 644. But the Owner can read and write. Everyone else tin only read. Nobody else tin can execute this file.
- 655. Merely the Owner can read and write and cannot execute the file. Nobody else tin read and run and cannot change the file.
For instance, 777 means all users can Read, Write, and Execute. Because it gives full permission, you should use information technology with attending. However, in some cases, you'll require to set the 777 permissions before yous tin can upload one file to the server. Like this example, to change files permissions Linux:
How to recursively set permissions Linux
To change files permissions on Linux, we also tin do it recursively run on all files and folders below the given directory, use the -R (–recursive) pick:
And then, to modify the rights of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 755, you would utilize:
Discover files and modify permissions Linux
Allow'south imagine that y'all are working to set up some permissions on a web server. Y'all effigy out that the files are configured with the incorrect permission by assuasive anyone to change them.
The nigh straightforward approach to fix all files permission on a single control line is doing it recursively. To accomplish that goal, nosotros tin combine thediscovercommand withchmod.
Using the numeric method:
Outset, applying 644 on files:
find /var/www/bitslovers -blazon f -exec chmod 644 {} ; 2d, utilise 755 to the folder:
observe /var/www/bitslovers -type d -exec chmod 755 {} ; Using the symbolic method:
find /var/www/bitslovers -type f -exec chmod u=rw,go=r {} ; find /var/www/bitslovers -type d -exec chmod u=rwx,become=rx {} ; The find command volition seek files and folders beneath /var/www/bitslovers and motion each found file and folder to thechmodcommand to apply for the permissions.
How to modify the file permission using the Xargs control?
Another skilful example using xargs:
sudo find /var/www/bitslovers -type d -print0 | xargs -0 sudo chmod 755
How to preserve the permission on copy File or Directory?
Sometimes, when you are copying files on Linux, we take intendance of the permission besides. For example, suppose you are working on maintenance on the server using the root user. And, you need to move or copy files/folders from one specific awarding that merely one user is allowed to access. In this instance, you need to make sure not to change the permission from that files.
To attain that goal, we can use the selection-pfrom the cp control. Post-obit the case below:
cp -rp ~/bitslovers /var/www
Alternatively, y'all tin can utilize the selection-athat includes the -r flag and preserves everything.
How to preserve the permission on copy File or Directory using scp ?
Likewise, if you are transferring the files to a remote host, the option-pto preserve the permission also it'southward bachelor:
How to change symbolic link permissions
Symbolic links always hold 777 permissions.
Also, when changing the symlink's permissions, thechmodwill modify the permissions on the file where the link is pointing.
chmod 755 <symbolic-file-proper noun>
The odds are that rather than modifying the target ownership, yous volition get an error message "cannot access 'symlink': Permission denied."
The fault happens because, on most Linux distributions, symlinks are shielded and cannot manipulate target files. This configuration is defined in /proc/sys/fs/protected_symlinks.
In other words,1 ways immune and 0 not. Information technology is encouraged not to disable the symlink security.
Irresolute File Ownership in Linux
Changing file ownership in Linux could hands exist achieved by applying thechowncommand. For example: Assume we needed to alter the Possessor of backup.zip from i user to some other:
sudo chown <user-name> backup.zip
Where <user-proper noun> is the new Possessor.
Changing Grouping Buying in Linux
Likewise, it's possible to change the Group that owns that file:
chgrp <grop-name> backup.zip
Where <group-name> is the new Possessor Group.
Tip
Suppose you are working on reviewing multiples files to fix the permission. Then, y'all tin execute the find command to detect files that match with specific permission. So, this way, you can browse your computer or binder to inspect the file's permission easily.
In this example, you can find all files configured with 777 permission and fix them speedily.
Conclusion
Change files permissions on Linux or define them tin can give you a roadblock if they're not ready rightly. Wrong permission sets could compromise the whole system. Though, if you'd adopt to reach a file on your arrangement or server, studying how to modify specific permissions is a must-have topic.
Too, you learned that chmod 777 is the command you'll utilize to configure a file or folder bachelor to everyone. And, it would be all-time if you used it in limited circumstances and turnabout back to a more than restrictive set of permissions once you're finished.
To read more than about chmod, visit the chmod man page.
Source: https://www.bitslovers.com/change-files-permissions-on-linux/
0 Response to "Change Permissions Linux Folder to Upload Files"
Post a Comment